
The environmental impact of vehicles has become a critical topic as the world seeks to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. Gasoline-powered vehicles and electric vehicles (EVs) represent two divergent paths in terms of environmental sustainability. This article explores and compares their environmental impacts through a series of questions and answers.
Q1: What are the primary differences in greenhouse gas emissions between gasoline and electric vehicles?
A: Gasoline vehicles emit greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter directly from their tailpipes during operation. In contrast, electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions when powered purely by electricity. However, it’s essential to consider emissions from electricity generation, which varies depending on the energy mix of the grid.
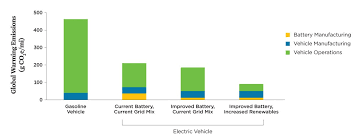
Q2: How do the overall emissions compare over the lifetime of gasoline and electric vehicles?
A: The lifecycle emissions of vehicles include emissions from manufacturing, fuel production, operation, and disposal. Studies generally show that electric vehicles, even when accounting for manufacturing emissions and electricity generation, have lower lifecycle emissions compared to gasoline vehicles, particularly in regions with a cleaner energy mix.
Q3: What is the environmental impact of battery production for electric vehicles?
A: Battery production for electric vehicles involves mining and processing raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can have environmental impacts. However, advancements in battery technology and recycling processes are reducing these impacts. The overall environmental impact of batteries is typically outweighed by the emissions savings during vehicle operation.

Q4: How does the energy efficiency of gasoline vehicles compare to electric vehicles?
A: Gasoline vehicles typically have lower energy efficiency compared to electric vehicles. Internal combustion engines (ICEs) convert only about 20-30% of the energy from gasoline into mechanical power for propulsion. Electric vehicles, on the other hand, are more efficient, converting about 60-70% of electrical energy into driving power.
Q5: What role does renewable energy play in reducing the environmental impact of electric vehicles?
A: The environmental benefits of electric vehicles are enhanced when they are charged using electricity generated from renewable sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. In regions with a high proportion of renewable energy in the grid mix, EVs effectively have zero operational emissions, significantly reducing their overall environmental footprint.

Table: Environmental Impact Comparison of Gasoline and Electric Vehicles
| Aspect | Gasoline Vehicles | Electric Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| Tailpipe Emissions | Emit CO2, NOx, particulate matter | Zero tailpipe emissions |
| Lifecycle Emissions | Higher, including fuel extraction and refining | Lower, especially in regions with cleaner energy sources |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient (~20-30% energy conversion) | More efficient (~60-70% energy conversion) |
| Battery Production | Involves mining and processing raw materials | Environmental impacts mitigated by recycling efforts |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Dependent on fossil fuels for operation | Benefits from zero emissions when charged with renewable energy |

Understanding the environmental impact of gasoline and electric vehicles is crucial for making informed decisions about transportation choices. As technology advances and renewable energy adoption increases, electric vehicles continue to emerge as a sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars, contributing to efforts towards a greener and more sustainable future.